Agile Application Life Cycle Management: Accelerating Modern Software Delivery
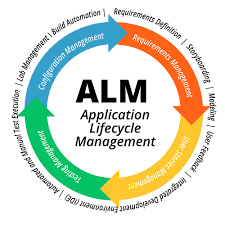
Agile Application Life Cycle Management (ALM) refers to the coordinated management of people, processes, and tools used to plan, develop, test, deploy, and maintain software applications in an agile environment. Unlike traditional ALM approaches that follow rigid, sequential phases, agile ALM emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and continuous improvement. It aligns closely with agile methodologies such as Scrum, Kanban, and DevOps, enabling organizations to respond quickly to changing business requirements while maintaining high software quality.
At its core, agile ALM integrates all stages of the application lifecycle into a unified and iterative workflow. Planning begins with clearly defined user stories, backlogs, and sprint goals that reflect customer and business priorities. Requirements are not treated as static documents but evolve continuously based on feedback and insights gained during development. This adaptive planning approach ensures that teams focus on delivering the most valuable features first, reducing waste and improving overall project outcomes.
Development in agile ALM is highly collaborative and incremental. Cross-functional teams work in short development cycles, or sprints, to design, code, and refine application features. Frequent code integration, supported by version control systems, helps identify issues early and promotes transparency across teams. Developers, testers, and product owners collaborate closely, ensuring that functionality aligns with expectations and can be adjusted rapidly when priorities change.
Testing is embedded throughout the agile ALM process rather than being confined to a single phase. Continuous testing, including automated unit, integration, and regression tests, allows teams to detect defects early and maintain consistent application quality. This approach reduces the risk of late-stage failures and supports faster release cycles. By integrating testing into every sprint, organizations can confidently deliver stable and reliable software at a rapid pace.
Deployment and release management are also streamlined within agile ALM. Continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) practices enable frequent and predictable releases, often with minimal manual intervention. Feedback from end users and stakeholders is collected after each release and fed back into the planning process, creating a closed-loop system of improvement. This continuous feedback mechanism helps organizations align software development closely with real-world usage and business goals.
Agile ALM also plays a critical role in application maintenance and optimization. Post-deployment activities such as monitoring, performance analysis, and issue resolution are managed within the same lifecycle framework. Teams can quickly address bugs, enhance features, and adapt applications to new technologies or regulatory requirements. This holistic view of the application lifecycle ensures long-term value and sustainability.
In today’s fast-paced digital environment, agile Application Life Cycle Management has become essential for organizations seeking faster time-to-market, improved collaboration, and higher customer satisfaction. By unifying planning, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance within an agile framework, agile ALM empowers teams to deliver high-quality software that evolves continuously with business needs.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jeux
- Gardening
- Health
- Domicile
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Autre
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness